Vroom-Jago Decision Model
What's it for?
The Vroom-Jago decision model is a rational model used by leaders to determine whether they should make a decision alone or involve a group, and to what extent the group should be involved.
This method was first proposed by Vroom and Yetton in 1973 and was later modified by Vroom and Jago in 1988. Subsequent studies have shown that the greater precision in situational assessment of the Vroom-Jago decision model allows for better discrimination in choosing a process.
In some business situations it's better for a leader to be the decision maker for the group. In others, it's best for the group to have some input or even make the decision. This model distinguishes five different situations and outlines an algorithm for determining which one to use.
The 5 processes
Autocratic l (Al)
You, the decision maker, use the information available to make the decision yourself.
Autocratic ll (A2)
You request information from members of your team. They may or may not know why you want such information. They neither define the situation, alternatives or final choice.
Consultative l (Cl)
You explain the situation to the individual members of the group but they do not get together as a group. You make the final decision.
Consultative ll (C2)
There is group discussion where you explain the situation and gather ideas and suggestions. Again, you're responsible for the final decision making.
Group ll (G2)
The group as a whole make the decision. You as the leader present the situation and the group defines alternatives and reaches a consensus decision. The leader acts more as a facilitator in this process and allows the group to agree on the final choice.
Which one?
The Vroom-Jago decision model uses a series of seven questions, asked in order, to determine which of these five processes to use. This is a somewhat prescriptive process and allows you to move through the diagram below. On reaching the right-hand side, the indicated process is the most appropriate for your situation.
The 7 questions
- Is high quality important here or is a good solution absolutely critical? (is this a case where it would not be acceptable having lots of equal alternatives?)
- As the leader, do you have enough information of your own to make a good decision?
- Is the problem structured in that it is clearly defined, organized and has recognized solutions?
- Do the members of the group have to accept this decision for it to work?
- If you make this decision yourself, are you sure the group will accept it?
- Are the group members aligned with the same goals that you are trying to achieve?
- Is disagreement likely among group members in reaching a decision?
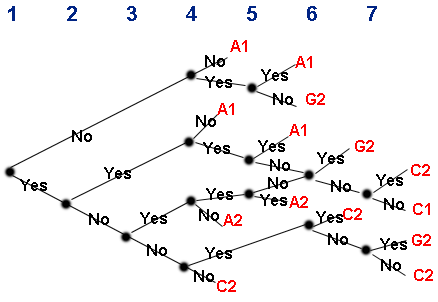
In the example, if the quality requirement is not high, choose the upper limb. With regards to question 4, if they have to accept it, choose 'yes'. Then 'yes' again if you know they will accept your decision. This points you at A1, so you go ahead and make the decision yourself.
Remember...
The Vroom-Jago decision model is itself a decision tree and will only be as useful as the quality of information you input and how you approach the decision itself...
Like this page?
Mind Control
You have probably noticed that I am moving the whole Mind Control section to a new site. Please excuse any inconvenience. I expect to have made the whole move in the next few days.
This is the new site www.pschobegone.com. Feel free to come and visit. Any suggestions will be gratefully received!